Single-shot hyperspectral wavefront imaging
Blochet, B., N. Lebas, P. Berto, D. Papadopoulos, and M. Guillon
Nature Communications 17, no. 1 (2026)

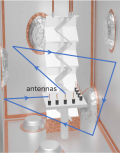
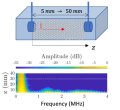
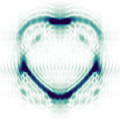
Résumé: Single-shot hyperspectral wavefront sensing is essential for applications like spatio-spectral coupling metrology in high-power laser or fast material dispersion imaging. Under broadband illumination, traditional wavefront sensors assume an achromatic wavefront, which makes them unsuitable. We introduce a hyperspectral wavefront sensing scheme based on the Hartmann wavefront sensing principles, employing a multicore fiber as a Hartmann mask to overcome these limitations. Our system leverages the angular memory effect and limited spectral correlation width of the multicore fiber, encoding wavefront gradients into displacements and the spectral information into uncorrelated speckle patterns. This method retains the simplicity, compactness, and single-shot capability of conventional wavefront sensors, with only a slight increase in computational complexity. It also allows a tunable trade-off between spatial and spectral resolution. We demonstrate its efficacy for recording the hyperspectral wavefront cube from single-pulse acquisitions at the Apollon multi-petawatt laser facility, and for performing multispectral microscopic imaging of dispersive phase objects.
|
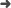
|
Computing leaky waves in semi-analytical waveguide models by exponential residual relaxation
Gravenkamp, H., B. Plestenjak, and D. A. Kiefer
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 452, 118763 (2026)

Résumé: Semi-analytical methods for modeling guided waves in structures of constant cross-section yield frequency-dependent polynomial eigenvalue problems for the wavenumbers and mode shapes. Solving these eigenvalue problems over a range of frequencies results in continuous eigencurves. Recent research has shown that eigencurves of differentiable parameter-dependent eigenvalue problems can alternatively be computed as solutions to a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) obtained by postulating an exponentially decaying residual of a modal solution. Starting from an approximate initial guess of the eigenvalue and eigenvector at a given frequency, the complete eigencurve is obtained using standard numerical ODE solvers. We exploit this idea to develop an efficient method for computing the dispersion curves of plate structures coupled to unbounded solid or fluid media. In these scenarios, the approach is particularly useful because the boundary conditions give rise to nonlinear terms that severely hinder the application of traditional solvers. We discuss suitable approximations of the nonlinearity for obtaining initial values, analyze computational costs and robustness of the proposed algorithm, and verify results by comparison against existing methods.
|
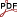
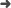
|
Acoustic transparency and absorption in dense granular suspensions
Tourin, A., Y. Abraham, M. Palla, A. Le Ber, R. Pierrat, N. Benech, C. Negreira, and X. Jia
Physical Review E 113, no. 2 (2026)

Résumé: We demonstrate the existence of a frequency band exhibiting acoustic transparency in two- and three-dimensional dense granular suspensions, enabling the transmission of a low-frequency ballistic wave excited by a high-frequency broadband ultrasound pulse. This phenomenon is attributed to spatial correlations in the structural disorder of the medium. To support this interpretation, we use an existing model that incorporates such correlations via the structure factor. Its predictions are shown to agree well with those of the generalized coherent potential approximation (GCPA) model, which is known to apply at high volume fractions, including the close packing limit, but does not explicitly account for disorder correlation. Within the transparency band, attenuation is found to be dominated by absorption rather than scattering. Measurements of the frequency dependence of the absorption coefficient reveal significant deviations from conventional models, challenging the current understanding of acoustic absorption in dense granular media.
|
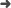
|
Attenuation and dispersion of coherent Rayleigh and head waves on the surface of a polycrystal
Du Burck, C., and A. Derode
The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 159, no. 1, 955-973 (2026)

Résumé: This work presents experimental and theoretical results concerning the dispersion and attenuation caused by scattering during the propagation of ultrasonic waves on the surface of a polycrystal. Rayleigh and head waves are measured in the case of two Inconel® 600 samples with different average grain sizes. The coherent, i.e., ensemble-averaged, waves are estimated, as well as their frequency-dependent phase velocities and scattering mean-free paths. The results obtained from a contactless laser setup are compared to those obtained from a transducer array placed on the surface of the sample. The influence of contact is highlighted, particularly at low frequency and in the small-grained sample, where the attenuation by scattering is lower. Moreover, the two-point correlation (TPC) functions of both samples are estimated, and it is shown that neither is exponential. Standard theoretical models are adapted to these particular TPCs and yield effective bulk wavenumbers, from which effective surface wavenumbers can be calculated via a simple and approximate method. The theoretical results are then compared to the experimental ones.
|
|
Guiding waves through chaos: Universal bounds for targeted mode transport
Wang, C. Z., J. Guillamon, U. Kuhl, M. Davy, M. Reisner, A. Goetschy, and T. Kottos
Science Advances 12, no. 5, eaeb1158 (2026)

Résumé: Controlling wave propagation in complex environments is a central challenge across wireless communications, imaging, and acoustics, where multiple scattering and interference obscure direct transmission paths. Coherent wavefront shaping enables precise energy delivery but typically requires full knowledge of the medium. Here, we introduce a universal statistical framework for targeted mode transport (TMT) that circumvents this limitation and validate it on various platforms including microwave networks, two-dimensional chaotic cavities, and three-dimensional reverberation chambers. TMT quantifies the efficiency of transferring energy between specified input and output channels in multimode wave-chaotic systems. We develop a diagrammatic theory that predicts the eigenvalue distribution of the TMT operator and identifies the macroscopic parameters-coupling strength, absorption, and channel control-that govern performance. The theory provides explicit bounds for optimal TMT wavefronts and captures phenomena like statistical transmission gaps and reflectionless states. These findings establish design principles for energy delivery and information transfer in complex environments, with broad implications for adaptive signal processing and wave-based technologies.
|
|
Homogenization of resonant bubble screens: Influence of bubble shape and lattice arrangement
Pham, K., and A. Maurel
Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 159, no. 1, 357-372 (2026)

Résumé: A time-domain effective model for acoustic wave propagation through a two-dimensional periodic array of gas bubbles embedded in a liquid is presented. The model is expressed as transmission conditions: pressure remains continuous, whereas the normal velocity exhibits a jump induced by the internal pressure of the bubbles. This internal pressure follows a damped mass–spring equation, with damping arising solely from radiative coupling to the surrounding liquid, which makes the resonance frequency and quality factor of the array emerge unambiguously. Aside from the bubble density in the lattice, these quantities are fully governed by two independent geometric parameters: a dimensionless capacitance, depending solely on bubble shape, and a lattice coefficient, depending solely on lattice geometry. For plane wave scattering, comparisons with direct numerical simulations demonstrate that the model accurately reproduces the resonant behavior of bubble screens across a range of configurations, including spherical, spheroidal, and cylindrical bubbles, as well as square and rectangular lattices. This generalizes the classical model of Leroy et al. [Eur. Phys. J. E 29(1), 123–130 (2009)] for spherical bubbles in square lattices. Notably, the model reveals—and simulations confirm—that the resonance frequency shift relative to an isolated bubble, usually positive (blue shift), can become negative (red shift) in rectangular lattices with aspect ratios exceeding seven.
|
|